CloudFormation ACM Certificate Automation
The problem with the ACM certificate in CloudFormation requires manual configuration in an additional layer outside of CloudFormation, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Additionally, changes to the certificate may not be reflected in CloudFormation, making it difficult to maintain up-to-date configurations.
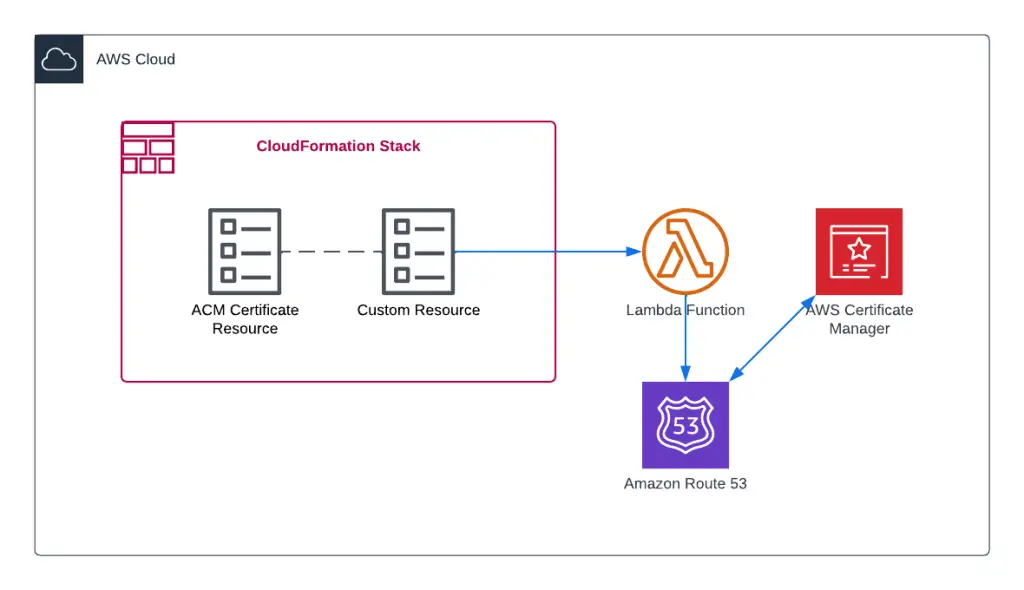
This CloudFormation ACM Certificate automation guide demonstrates using CloudFormation custom resources to automate ACM SSL certificate validation using DNS.
Table of contents
Here’s the list of technologies to be used:
- Python 3
- Boto3
- CloudFormation.
The final version of the AWS CloudFormation template is available on GitHub.
Automation process
Let’s start automating our task from the simple AWS CloudFormation template, which creates the AWS Certificate Manager(ACM) Certificate resource requests with resources such as ACMCertificate, Certificate Domain name(same domain as your site), Subject alternative name extension, enables secure connections, etc. Know that the logging preference in this template is enabled and already has a specified certificate transparency logging preference.
ACM Certificate resource
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: >
This CloudFormation template validates ACM certificate
using AWS Route53 DNS service.
Parameters:
Route53HostedZoneName:
Type: String
DomainName:
Type: String
Resources:
ACMCertificate:
Type: AWS::CertificateManager::Certificate
Properties:
DomainName: !Ref DomainName
SubjectAlternativeNames:
- !Sub "*.${DomainName}"
ValidationMethod: DNS
Outputs:
ACMCertificateArn:
Value: !Ref ACMCertificate
As soon as we try to create a stack from this template, we’ll immediately see, that in the Events section of our stack, there’s a Status reason field for ACMCertificate resource(should only be a public certificate and not a private certificate authority), which contains the following message:
Content of DNS Record is: {Name: _8c764e0f4e100a01c2d710674388e7d7.awsam.hands-on.cloud.,Type: CNAME,Value: _f10faf50b877f1c7d80cf6c26535acd8.kirrbxfjtw.acm-validations.aws.}This message can be used to automate Route53 records creation during stack deployment. And CloudFormation custom resources will help us with this part.
CloudFormation custom resource
To solve the problem in general, we need the following information:
- Stack name – we’ll use Python boto3 library to get access to CloudFormationevents to parse for required DNS validation records (Domain validation records).
- Route53 Hosted Zone name – we’ll use the Python Boto3 library to create necessary DNS records in our Hosted Zone.
Let’s extend our template with the required resources:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: >
This CloudFormation template validates ACM certificate
using AWS Route53 DNS service.
Parameters:
Route53HostedZoneName:
Type: String
DomainName:
Type: String
Resources:
ACMCertificate:
Type: AWS::CertificateManager::Certificate
Properties:
DomainName: !Ref DomainName
SubjectAlternativeNames:
- !Sub "*.${DomainName}"
ValidationMethod: DNS
ACMCertificateValidationResource:
Type: Custom::ACMCertificateValidation
Properties:
ServiceToken: !GetAtt ACMLambdaFunction.Arn
Route53HostedZoneName: !Ref Route53HostedZoneName
StackName: !Ref 'AWS::StackName'
ACMLambdaFunctionRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- lambda.amazonaws.com
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Path: "/"
Policies:
- PolicyName: root
PolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- logs:CreateLogGroup
- logs:CreateLogStream
- logs:PutLogEvents
Resource: '*'
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- route53:ChangeResourceRecordSets
- route53:ListHostedZonesByName
- cloudformation:DescribeStackEvents
Resource: '*'
ACMLambdaFunction:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Function
Properties:
Runtime: python3.7
Timeout: '300'
Handler: index.handler
Role: !GetAtt ACMLambdaFunctionRole.Arn
Code:
ZipFile:
!Sub
- |-
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import cfnresponse
import boto3
import logging
import traceback
CFN_CLIENT = boto3.client('cloudformation')
LOGGER = logging.getLogger()
LOGGER.setLevel(logging.INFO)
def handler(event, context):
try:
LOGGER.info('Event structure: %s', event)
except Exception as e:
LOGGER.error(e)
traceback.print_exc()
finally:
cfnresponse.send(event, context, cfnresponse.SUCCESS, {})
-
stack_name: !Ref 'AWS::StackName'
acm_certificate_resource_arn: !Ref ACMCertificate
Outputs:
ACMCertificateArn:
Value: !Ref ACMCertificateCreating CloudFormation Stack from this template will create a custom resource ACMCertificateValidationResource backed by ACMLambdaFunction, which right now has very basic logic – instantiate required libraries, Boto3 CloudFormation client, and print us event object, which handles parameters passed to ACMLambdaFunction.
{
"RequestType": "Create",
"ServiceToken": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:819962779546:function:cfm-r53-test-ACMLambdaFunction-NI4EAH0T5OUM",
"ResponseURL": "https://cloudformation-custom-resource-response-useast1.s3.amazonaws.com/arn%3Aaws%3Acloudformation%3Aus-east-1%3A819962779546%3Astack/cfm-r53-test/14c784d0-1631-11ea-adc9-0ed2247e0ea9%7CACMCertificateValidationResource%7Cbd5a9206-7029-4608-9083-724a292bc51a?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Date=20191204T005812Z&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&X-Amz-Expires=7200&X-Amz-Credential=AKIA6L7Q4OWT5LA3SVU2%2F20191204%2Fus-east-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Signature=37dbeb173ca5d32c899371aaf13da19cb73a2ec4a9f5945820b7bf64f265357c",
"StackId": "arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-1:819962779546:stack/cfm-r53-test/14c784d0-1631-11ea-adc9-0ed2247e0ea9",
"RequestId": "bd5a9206-7029-4608-9083-724a292bc51a",
"LogicalResourceId": "ACMCertificateValidationResource",
"ResourceType": "Custom::ACMCertificateValidation",
"ResourceProperties": {
"ServiceToken": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:819962779546:function:cfm-r53-test-ACMLambdaFunction-NI4EAH0T5OUM",
"Route53HostedZoneName": "awsam.hands-on.cloud",
"StackName": "cfm-r53-test"
}
}You may take a look at your Event object at CloudWatch Logs.
Every single time ACMCertificateValidationResource resource is created, and our Lambda function is called. So, all we need to do now is to automate Route53 DNS record creation.
Let’s get access to the CloudFormation stack event and grab Route53 DNS records information:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: >
This CloudFormation template validates ACM certificate
using AWS Route53 DNS service.
Parameters:
Route53HostedZoneName:
Type: String
DomainName:
Type: String
Resources:
ACMCertificate:
Type: AWS::CertificateManager::Certificate
Properties:
DomainName: !Ref DomainName
SubjectAlternativeNames:
- !Sub "*.${DomainName}"
ValidationMethod: DNS
ACMCertificateValidationResource:
Type: Custom::ACMCertificateValidation
Properties:
ServiceToken: !GetAtt ACMLambdaFunction.Arn
Route53HostedZoneName: !Ref Route53HostedZoneName
StackName: !Ref 'AWS::StackName'
ACMLambdaFunctionRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- lambda.amazonaws.com
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Path: "/"
Policies:
- PolicyName: root
PolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- logs:CreateLogGroup
- logs:CreateLogStream
- logs:PutLogEvents
Resource: '*'
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- route53:ChangeResourceRecordSets
- route53:ListHostedZonesByName
- cloudformation:DescribeStackEvents
Resource: '*'
ACMLambdaFunction:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Function
Properties:
Runtime: python3.7
Timeout: '300'
Handler: index.handler
Role: !GetAtt ACMLambdaFunctionRole.Arn
Code:
ZipFile:
!Sub
- |-
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import cfnresponse
import boto3
import logging
import traceback
CFN_CLIENT = boto3.client('cloudformation')
LOGGER = logging.getLogger()
LOGGER.setLevel(logging.INFO)
def get_route53_record_from_stack_events():
status_reason_text = ''
params = {'StackName': '${stack_name}'}
while True:
cfn_response = CFN_CLIENT.describe_stack_events(**params)
LOGGER.info('Stack events: %s', cfn_response)
for event in cfn_response['StackEvents']:
if (
event['ResourceType'] == 'AWS::CertificateManager::Certificate' and
event['ResourceStatus'] == 'CREATE_IN_PROGRESS' and
'ResourceStatusReason' in event and
'Content of DNS Record' in event['ResourceStatusReason']
):
status_reason_text = event['ResourceStatusReason']
if 'NextToken' in cfn_response:
params['NextToken'] = cfn_response['NextToken']
if status_reason_text != '':
break
_dns_request_text=status_reason_text[status_reason_text.find("{")+1:status_reason_text.find("}")]
_name_text = _dns_request_text.split(',')[0]
_type_text = _dns_request_text.split(',')[1]
_value_text = _dns_request_text.split(',')[2]
return {
'Name': _name_text.split(': ')[1],
'Type': _type_text.split(': ')[1],
'Value': _value_text.split(': ')[1]
}
def handler(event, context):
try:
LOGGER.info('Event structure: %s', event)
LOGGER.info('Route 53 record: %s', get_route53_record_from_stack_events())
except Exception as e:
LOGGER.error(e)
traceback.print_exc()
finally:
cfnresponse.send(event, context, cfnresponse.SUCCESS, {})
-
stack_name: !Ref 'AWS::StackName'
Outputs:
ACMCertificateArn:
Value: !Ref ACMCertificateHere we used the describe_stack_events call to get all events from our stack and looped through all of them till we found the right one, which contains the Content of the DNS Record. Next, we parsed the event string and formed the following Python Dictionary:
{
"Name": "_8c764e0f4e100a01c2d710674388e7d7.awsam.hands-on.cloud.",
"Type": "CNAME",
"Value": "_f10faf50b877f1c7d80cf6c26535acd8.kirrbxfjtw.acm-validations.aws."
}At this point, you should see the following line in the CloudWatch Logs of your Lambda function:
Route 53 record: {'Name': '_8c764e0f4e100a01c2d710674388e7d7.awsam.hands-on.cloud.', 'Type': 'CNAME', 'Value': '_f10faf50b877f1c7d80cf6c26535acd8.kirrbxfjtw.acm-validations.aws.'}Complete example
Now, all we have to do is to modify our lambda function and create a Route53 record:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: >
This CloudFormation template validates ACM certificate using AWS Route53 DNS
service.
Parameters:
Route53HostedZoneName:
Type: String
DomainName:
Type: String
Resources:
ACMCertificate:
Type: 'AWS::CertificateManager::Certificate'
Properties:
DomainName: !Ref DomainName
SubjectAlternativeNames:
- !Sub '*.${DomainName}'
ValidationMethod: DNS
ACMCertificateValidationResource:
Type: 'Custom::ACMCertificateValidation'
Properties:
ServiceToken: !GetAtt ACMLambdaFunction.Arn
Route53HostedZoneName: !Ref Route53HostedZoneName
StackName: !Ref 'AWS::StackName'
ACMLambdaFunctionRole:
Type: 'AWS::IAM::Role'
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- lambda.amazonaws.com
Action:
- 'sts:AssumeRole'
Path: /
Policies:
- PolicyName: root
PolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- 'logs:CreateLogGroup'
- 'logs:CreateLogStream'
- 'logs:PutLogEvents'
Resource: '*'
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- 'route53:ChangeResourceRecordSets'
- 'route53:ListHostedZonesByName'
- 'cloudformation:DescribeStackEvents'
Resource: '*'
ACMLambdaFunction:
Type: 'AWS::Lambda::Function'
Properties:
Runtime: python3.7
Timeout: '300'
Handler: index.handler
Role: !GetAtt ACMLambdaFunctionRole.Arn
Code:
ZipFile: !Sub
- |-
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import cfnresponse
import boto3
import logging
import traceback
CFN_CLIENT = boto3.client('cloudformation')
ROUTE53_CLIENT = boto3.client('route53')
LOGGER = logging.getLogger()
LOGGER.setLevel(logging.INFO)
def get_route53_record_from_stack_events(stack_name):
status_reason_text = ''
params = {'StackName': stack_name}
while True:
cfn_response = CFN_CLIENT.describe_stack_events(**params)
LOGGER.info('Stack events: %s', cfn_response)
for event in cfn_response['StackEvents']:
if (
event['ResourceType'] == 'AWS::CertificateManager::Certificate' and
event['ResourceStatus'] == 'CREATE_IN_PROGRESS' and
'ResourceStatusReason' in event and
'Content of DNS Record' in event['ResourceStatusReason']
):
status_reason_text = event['ResourceStatusReason']
if 'NextToken' in cfn_response:
params['NextToken'] = cfn_response['NextToken']
if status_reason_text != '':
break
_dns_request_text=status_reason_text[status_reason_text.find("{")+1:status_reason_text.find("}")]
_name_text = _dns_request_text.split(',')[0]
_type_text = _dns_request_text.split(',')[1]
_value_text = _dns_request_text.split(',')[2]
return {
'Name': _name_text.split(': ')[1],
'Type': _type_text.split(': ')[1],
'Value': _value_text.split(': ')[1]
}
def handler(event, context):
try:
LOGGER.info('Event structure: %s', event)
if event['RequestType'] == 'Create':
stack_name = event['ResourceProperties']['StackName']
hosted_zone_name = event['ResourceProperties']['Route53HostedZoneName']
route53_record = get_route53_record_from_stack_events(stack_name)
LOGGER.info('Route 53 record: %s', route53_record)
route53_response = ROUTE53_CLIENT.list_hosted_zones_by_name(DNSName=hosted_zone_name)
hosted_zone_id = route53_response['HostedZones'][0]['Id']
route53_request_params = {
'HostedZoneId': hosted_zone_id,
'ChangeBatch': {
'Changes': [
{
'Action': 'UPSERT',
'ResourceRecordSet': {
'Name': route53_record['Name'],
'Type': route53_record['Type'],
'TTL': 60,
'ResourceRecords': [
{
'Value': route53_record['Value']
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
LOGGER.info('Route 53 request params: %s', route53_request_params)
ROUTE53_CLIENT.change_resource_record_sets(**route53_request_params)
except Exception as e:
LOGGER.error(e)
traceback.print_exc()
finally:
cfnresponse.send(event, context, cfnresponse.SUCCESS, {})
- stack_name: !Ref 'AWS::StackName'
Outputs:
ACMCertificateArn:
Value: !Ref ACMCertificateAnd finally, we added the Boto3 Route53 client, which allowed us to use the change_resource_record_sets call to create and/or modify.
Summary
In this article, we walked through the step-by-step process of CloudFormation ACM certificate request automation in the CloudFomation template using the custom resource.
